Ocean sciences, Geology
|
Oceans are covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface and contain 97% of the Earth's water. Nowadays, oceanographers have explored only ~5% of the World Ocean. We know the surface of the moon with more details than the bottom of our oceans.
"Oceanography" is a general term for ocean sciences and regroups mainly four different branches:
This website is essentially focused on Marine Geology. But we will also present some of the interactions between marine geology and other ocean sciences, e.g. Marine Biogeology, . Marine Geology can be subdivided between (i) deep sea geology, the study of the oceanic lithosphere and (ii) continental shelf and margins geology, where the lithosphere is composed of continental crust. |
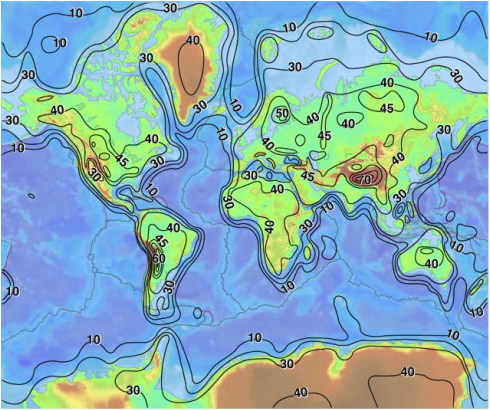
Isostasy, Oceanic crust vs continental crustOceanic and continental crusts are fundamentally different: the oceanic crust is mostly composed of basalts, it is significantly thinner (~8-10km) and denser (2.9 g/cm3) than the continental crust with its andesitic average composition (~30-50km; 2.7 g/cm3). These different physical properties explain why the average depth of the oceanic seafloor is lower than the continent surface.
The earth's lithosphere and its tectonic plates are "floating" on the asthenosphere. At isostatic equilibrium, since the continental crust is thicker and less dense, it floats higher than the oceanic crust. Isostasy refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium of the lithosphere. It can be simply illustrated by the principal of buoyancy, where an object immersed in a liquid is buoyed with a force equal to the weight of the displaced liquid. This simple process explains why the oceanic crust form deep basins between continents highs. Since water on earth exist at the liquid state, it is mostly found on top of the oceanic crust. |
Earth is a unique case in the solar system: it is the only terrestrial planet with a bimodal crust: continental vs oceanic crust. If compared to its sister planet Venus (roughly the same diameter), this feature is particularly striking. Venus topography appears singularly flat compared to our planet with nearly 51% of the surface located within 500 meters of the median radius and only 2% of the surface located at elevations greater than 2 kilometers. The dichotomy of Earth's crust is classically interpreted as a result of the existence and persistence of plate tectonic over geological ages.
Birth, life and Death of the Oceanic crust.
Mid-Oceanic Ridges (from the mantle to the surface).
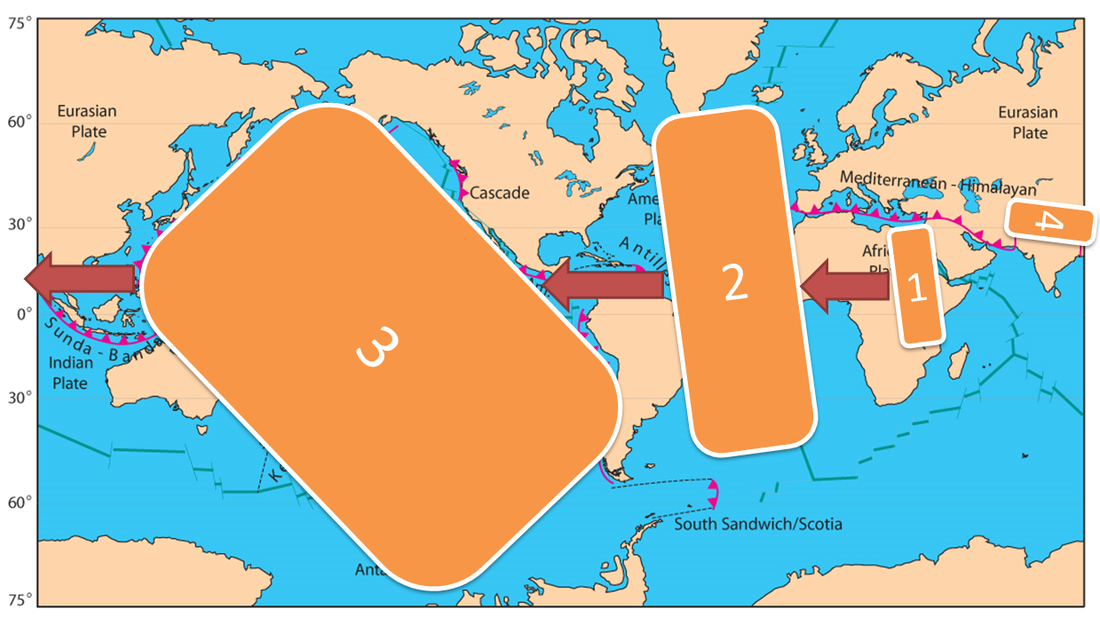
Subduction zones (from the surface back to the mantle).
Subduction zones (from the surface back to the mantle).